Esto es muy interesante, aunque lo que hace es abrirme mas dudas



Revisemos el análisis del ejemplo
4D - M - 8bits (1 byte) \
45 - E - 8bits (1 byte) |
4E - N - 8bits (1 byte) |
55 - U - 8bits (1 byte) |
45 - E - 8bits (1 byte) > Magic Word
54 - T - 8bits (1 byte) |
30 - 0 - 8bits (1 byte) |
31 - 1 - 8bits (1 byte) /
01 - 8bits (1 byte) \
00 - 8bits (1 byte) |
00 - 8bits (1 byte) > header version - observo que esta almacenada al reves, no debo leer 01000000, debo leer 00000001
00 - 8bits (1 byte) /
24 - 8bits (1 byte) \
00 - 8bits (1 byte) \
00 - 8bits (1 byte) > address of START of code
00 - 8bits (1 byte) /
63 - 8bits (1 byte) \
01 - 8bits (1 byte) |
00 - 8bits (1 byte) > addres of END of code
00 - 8bits (1 byte) /
00 - 8bits (1 byte) \
00 - 8bits (1 byte) |
10 - 8bits (1 byte) > memory reserved
00 - 8bits (1 byte) /
F0 - 8bits (1 byte) \
FF - 8bits (1 byte) |
07 - 8bits (1 byte) > pointer to stack
00 - 8bits (1 byte) /
00 - 8bits (1 byte) \
00 - 8bits (1 byte) |
00 - 8bits (1 byte) > pointers to argv[0]
00 - 8bits (1 byte) /
00 - 8bits (1 byte) \
00 - 8bits (1 byte) |
00 - 8bits (1 byte) > pointers to argv[1]
00 - 8bits (1 byte) /
¿Hasta aquí es correcto?
¿debo seguir leyendo de 4bytes en 4 bytes? ¿Que es E8350000?
Resto del programa pendiente de analizar.... draw_window... llamadas al sistema...
E8350000006A0A58CD4083F801740C83F802740E83F8037410EBEAE81A000000EBE36A0258CD40EBDC6A1158CD4080FC01750583C8FFCD40EBCB6A0C5831DB43CD4031
C0BB2C016400B978006400BAFFFFFF14BEFF998880BF4F010000CD40BB23001900B966442200BAAE0000006A285E6A0458CD4083C30A83C228803A0075F36A0C586A025B
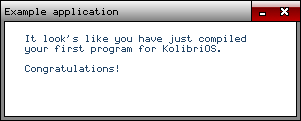
CD40C34974206C6F6F6B2773206C696B6520796F752068617665206A75737420636F6D70696C6564202020796F75722066697273742070726F6772616D20666F72204B6F6C6962
72694F532E2020202020202020202020202020202020202020202020202020202020202020202020202020202020202020202020436F6E67726174756C6174696F6E732120202020
2020202020202020202020202020202020202020004578616D706C65206170706C69636174696F6E00
 , ¿hay algún lugar donde explique que es cada byte code?
, ¿hay algún lugar donde explique que es cada byte code?